B30P105高磁硅钢变压器硅钢产品的真实面貌,远比文字描述来得丰富和生动。点击观看我们的视频,让产品自己为您讲述它的故事。
以下是:B30P105高磁硅钢变压器硅钢的图文介绍
鹿程国际贸易有限公司吸取和引进国内的先进技术与先进设备,汇集了一大批长期从事 安徽合肥汽车大梁钢研究、应用的工程技术人才,整合技术、人才优势。


电工钢硅钢片本文件按照 GB/T 1.1—2020《标准化工作导则 部分:标准化文件的结构和起草规则》的规定起草。本文件参考 IEC 60404-8-8:2017 进行编制。本文件代替 Q/BQB 481-2018。本文件与 Q/BQB 481-2018 相比,主要修改内容如下:——新增高强度型 AHV-M 产品;——新增高强度型 AHS 产品;——删除表 2 半有机无铬极厚涂层;——新增表 3 高强度型、安徽合肥高强度型二类产品磁性能和技术特性;——新增表 3 0.25mm 厚度规格产品;——删除表 3 型 B15AHV1000、安徽合肥B35AHV1900 牌号产品、安徽合肥高磁感型 B35APV1900 牌号产品;——新增表 3 高磁感型 B15APV1000、安徽合肥B20APV1200 牌号产品;——提高了表 3 部分牌号产品的磁极化强度标准;——新增表 4 高强度型和高强度型二类产品的力学性能标准;——修改绝缘涂层附着性评价级别代码;——加严了表 5 纵向厚度偏差标准;——加严了不平度标准;——删除内应力检测项目;——附录 A 删除了半有机无铬极厚涂层;——修订了附录 B;——修订附录 D 部分牌号产品的磁性能和力学性能典型值;——新增附录 D 高强度型和高强度型二类产品的磁性能和力学性能典型值;——修订附录 F 本文件与宝钢股份原薄规格牌号对照表


电工钢硅钢片应力退火电工钢在剪切、安徽合肥同城冲片和弯曲加工等机械变形作用下,电磁性能将发生劣化。为此进行应力退火,可以使电工钢的电磁性能恢复至原来水平。应力退火的条件和工艺将根据加工程度、安徽合肥同城退火炉况等有明显不同,用户务必注意如下几点:(1) 加热与冷却速度电磁性能一般不受加热和冷却速度的影响,但用户需确保材料不变形。(2)退火温度与保温时间取向电工钢退火温度在780-820℃之间较为适宜,为确保退火效果,退火材料应均热的保持,保温时间应根据铁芯形状、安徽合肥同城装炉量等进行调整。(3)防止渗碳与氧化由于渗碳及氧化会使电磁性能劣化,用户应充分注意炉内气体,并确保炉内气体的露点在较低状态。另外,为防止在退火中发生渗碳,应该在退火前,将铁芯加工过程中润滑油脂等有机化合物干净。同时,为确保退火效果,建议与炉内高温接触部分尽量采用低碳含量材料。有害物质限定承诺 宝钢的取向电工钢产品符合RoHS、安徽合肥同城REACH有害物质限定要求。



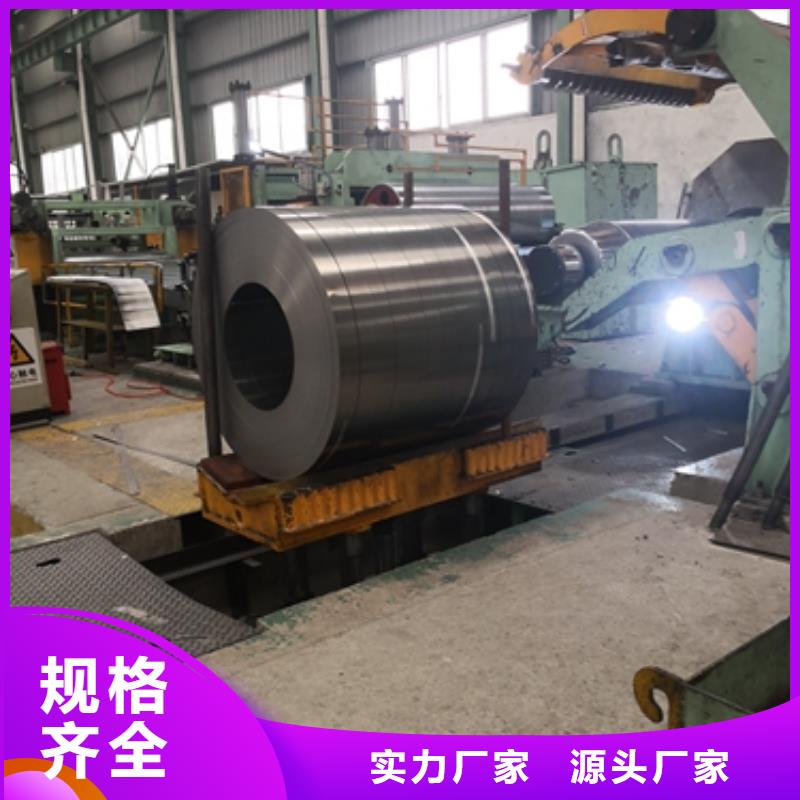
电工钢硅钢片硅钢是一种硅铁合金。用硅钢轧制的片材是电工领域中应用广的软磁材料,因而硅钢片又称电工钢片。硅钢片广泛用于电动机、发电机、变压器、扼流圈、电磁机构、继电器及测量仪表中电机工业大量使用厚度为0.35~0.50mm的硅钢片,用于:中型旋转机,压缩电机,通用马达,小型精密电机,电动汽车,压缩机,通用电机,电源变压器,精密变压器,节能电机,焊机变压器,稳压器,磁性密封器,加速器用电磁铁,汽车电机等;在电信高频技术中常用0.05~0.20mm的薄带钢片,以便更有效地降低涡流损耗。热轧硅钢片厚度为0.35~0.50mm,密度为7.55~7.70g/cm3,多用于大、中、小型交、直流电动机;冷轧无取向硅钢片厚度为0.35~0.50mm,密度为7.65~7.75g/cm3,多用于大型交流发电机、电动机,大、中、小型交、直流电动机;冷轧取向硅钢片厚度为0.23mm 0.27mm 0.3mm 0.35mm,密度为7.65g/cm3,多用于电力变压器、油浸式变压器,干式变压器,电抗器、磁放大器等;冷轧取向薄带厚度为0.05~0.20mm,多用于无线电高频变压器。


电工钢硅钢片Electrical steel, also known as silicon steel sheet, is an indispensable metal material in the power, electronics, and military industries, and is also the largest functional material in production. It is mainly used as the iron core for various motors, generators, and transformers. Specific total loss (iron loss) is the total power consumed per unit mass of material when the magnetic polarization waveform remains sinusoidal, with a specific peak and frequency. The specific total loss is represented by the symbol P (Jm/f), in W/kg. Example: P1.5/50 represents the specific total loss at a maximum magnetic polarization intensity of 1.5T and a frequency of 50Hz. 3.2 Magnetic Polarization Q/BQB 480-20212 Magnetic polarization intensity refers to the peak magnetic polarization intensity of a specific magnetic field intensity when a sample is subjected to alternating magnetization. Its symbol is J (H), and the unit is T (Tesla). Example: J5000 represents the peak magnetic polarization intensity corresponding to a magnetic field intensity peak of 5000A/m. The material grades in this document are classified based on the nominal maximum specific total loss P1.5/50 (W/kg) at a magnetic polarization strength of 1.5T and a frequency of 50Hz, as well as the nominal thickness of the material. They are further divided into three categories based on product characteristics: ordinary type, stress relief annealing type, and high-efficiency type. Example 1: B35A210 represents a common non oriented electrical steel with a nominal thickness of 0.35mm, and the maximum nominal specific total loss value P1.5/50 is 2.10W/kg; Example 2: B35AR300 represents a stress relieved annealed non oriented electrical steel with a nominal thickness of 0.35mm, and the maximum nominal specific total loss value P1.5/50 is 3.00W/kg; Example 3: B35AH230 represents an efficient non oriented electrical steel with a nominal thickness of 0.35mm, and the maximum nominal specific loss value P1.5/50 is 2.30W/kg. Example 4: 35WW210 represents a normal type WW non oriented electrical steel with a nominal thickness of 0.35mm, and the maximum nominal specific loss value P1.5/50 is 2.10W/kg. Example 5: 35WH230 represents an efficient WH non oriented electrical steel with a nominal thickness of 0.35mm, and the maximum nominal specific loss value P1.5/50 is 2.30W/kg. The classification and code of insulation coatings shall comply with the provisions of Table 2. Table 2 Classification and Code of Insulation Coatings Type Code Characteristics of Insulation Coatings Semi organic Thin Coating A Improves Punching Performance and Has Good Weldability Semi organic Thick Coating H has Good Punching Performance and High Interlayer Resistance Semi organic Chromium Free Thin Coating K does not contain chromium and has good weldability Semi organic Chromium Free Thick Coating M does not contain chromium and has good insulation performance Semi organic Chromium Free Extreme Thick Coating J does not contain chromium and has excellent insulation performance Semi organic Chromium Free Ultra Thick Coating L does not contain chromium and has extremely high insulation performance Self adhesive Coating







